Spice up your day with Chicken tikka masala and tandoor-made Naan on the side.
Untangling the Significance of Indian Cuisine: An Overview to Iconic Famous Indian Food
Indian cuisine is a complicated mosaic, characterized by its rich flavors and diverse local tastes. Each meal reflects an unique cultural heritage, mixing farming techniques with cookery. From the luscious gravies of the North to the rice-based specializeds of the South, the range is astounding. This exploration will certainly expose renowned meals and the tales behind them, in addition to the considerable function of street food in India's gastronomic landscape. What keys lie within this culinary custom?
The Abundant Tapestry of Indian Flavors
While numerous foods rely upon a minimal variety of flavors, Indian cuisine is identified by its comprehensive and varied range of seasonings. This abundant tapestry of seasonings consists of staples such as cumin, coriander, cardamom, and turmeric, each adding unique attributes to meals. Cumin offers a cozy, earthy taste, while coriander includes a tip of citrus. Cardamom, frequently described as the "queen of seasonings," imparts a wonderful, aromatic quality, and turmeric extract provides a dynamic gold hue in addition to its wellness benefits.
Seasonings are not simply spices in Indian cooking; they are vital to the culinary approach, symbolizing balance and harmony. The art of mixing seasonings, referred to as masala, varies from region to area, showcasing the cooking proficiency passed down via generations. This detailed usage of flavors not only enhances taste yet additionally shows India's cultural heritage, making each dish a sensory experience that narrates of its origin.
Regional Variations: Exploring the Diversity of Indian Recipes
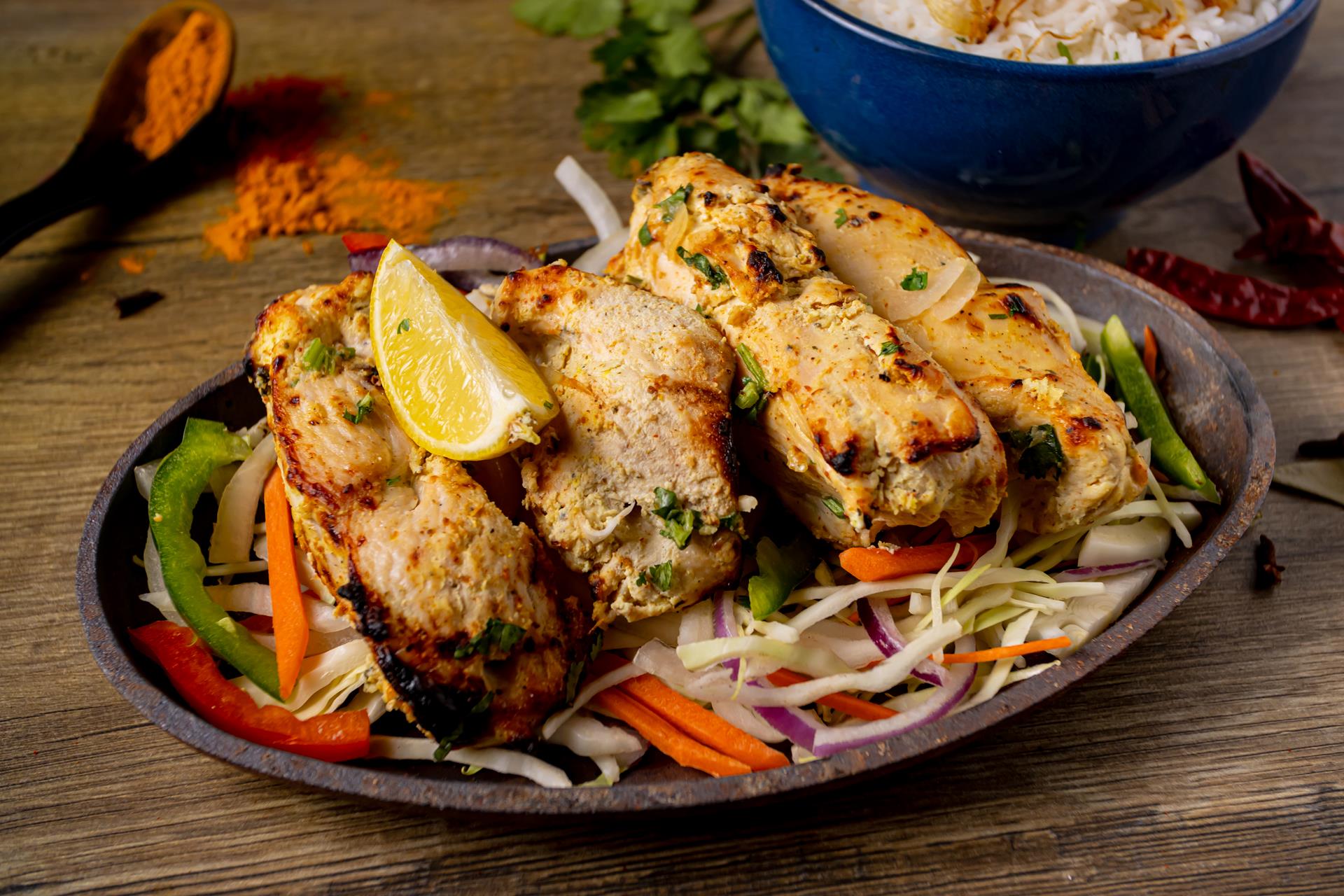
North vs. South Food
Although both South and north Indian foods share a rich heritage, they offer distinctive tastes, components, and cooking techniques that mirror their varied regional influences. North Indian food is characterized by its use milk products, such as paneer and ghee, and includes dishes like butter hen and naan. The cuisine typically integrates rich sauces and aromatic seasonings, dealing with a palette looking for comfort and heat. In contrast, South Indian food highlights rice, lentils, and fresh veggies, leading to lighter, tangy recipes like dosa and sambar. Coconut and curry leaves prevail, adding to its one-of-a-kind taste account. This regional divergence highlights the cooking breadth of India, showcasing exactly how location and culture form food traditions across the nation.
Flavors and Active Ingredients Diversity
The lively tapestry of Indian cuisine is woven with each other by an amazing selection of ingredients and flavors, each adding to the country's culinary variety. From the fiery chilies of the south to the aromatic cardamom of the north, these components vary regionally, mirroring local farming and climate. Coastal areas utilize fresh fish and shellfish and coconut, while arid areas favor lentils and grains. Using seasonings like coriander, turmeric extract, and cumin is ubiquitous, yet each region has its unique mix, such as garam masala or panch phoron. Furthermore, neighborhood herbs and veggies additionally enhance meals, showcasing seasonal availability. This elaborate interplay of textures and tastes is what makes Indian food both varied and deeply rooted in tradition.
Iconic Cuisines: From Biryani to Butter Hen
Rich in tastes and customs, legendary dishes such as biryani and butter chicken exemplify the diverse culinary landscape of the Indian subcontinent. Biryani, a fragrant rice meal layered with marinaded meat, showcases regional variations, from the spicy Hyderabadi to the tasty Lucknowi. Each version reflects local spices, cooking techniques, and cultural influences, making biryani a beloved meal across India.
Butter chicken, or murgh makhani, originates from Delhi and features tender hen items simmered in a luscious tomato sauce improved with seasonings and butter. This recipe highlights the combination of flavors, combining elements from Mughlai food with standard Indian cooking. Both dishes not only please the palate but also inform stories of India's rich background and the mixing of social influences. Together, they stand as demos of the virtuosity and intricacy of Indian additional reading cuisine, welcoming food fanatics to explore their distinct tastes and prep work.
The Art of Indian Street Food
Indian street food stands for a lively tapestry of appearances and tastes, charming residents and vacationers alike. This cookery form thrives in dynamic markets, where vendors skillfully prepare fast, cost effective, and tasty dishes. From the spicy and tasty pani puri to the tasty chaat, each dish uses a special taste experience, usually gone along with by a symphony of fragrant spices.
Road food is not merely concerning nourishment; it embodies the significance of social interaction and social exchange. Individuals collect around food stalls, sharing stories and laughter, creating a feeling of community. Regional variants add further deepness, with each area boasting its specialties, such as vada pav in Mumbai or kathi rolls in Kolkata.
The prep work techniques, usually passed down via generations, reflect a mix of practice and advancement. This dynamic street food scene shows the abundant cooking heritage of India, making it an essential part of the nation's identification.
Conventional Food Preparation Methods and Their Importance
Typical cooking strategies in Indian food mirror the diverse local practices and the cultural significance of food preparation. These techniques not only improve the flavors and appearances of ingredients however additionally personify routines that attach individuals to their heritage. Recognizing these strategies brightens the essential function they play in keeping authenticity and preserving cooking practices.
Regional Food Preparation Approaches
While discovering the varied landscape of cooking approaches, one can discover a tapestry of local methods that show the cultural heritage and neighborhood resources of various locations. Each area in India showcases one-of-a-kind methods, such as using clay pots in rural communities, which enhance taste via sluggish cooking. The tandoor method, widespread in the north, conveys an unique smokiness to breads and meats, while steaming is favored in seaside areas, protecting the freshness of fish and shellfish and veggies. In the south, solidifying spices in warm oil is a vital action, releasing essential oils and scents. These methods not just produce distinctive cooking identities but additionally link communities to their historical and ecological contexts, highlighting the significance of tradition in Indian food.
Component Prep Work Routines
In numerous kitchens throughout India, ingredient prep work routines play an essential function fit the culinary experience. These routines encompass numerous techniques, such as saturating lentils, grinding spices, and cutting vegetables, which boost textures and Extra resources tastes. Each step is usually steeped in practice, showing local preferences and seasonal schedule (Mango lassi). The precise grinding of seasonings in a stone mortar, recognized as 'sil batta', not just maintains vital oils yet also links chefs to their heritage. Additionally, the act of preparing active ingredients is commonly a communal affair, cultivating family members bonds and shared cultural worths. Inevitably, these rituals are not simply practical yet offer to honor the food, elevating the cooking process into an art type that commemorates India's abundant cooking heritage
The Global Influence of Indian Cuisine
As Indian cuisine continues to acquire popularity worldwide, its abundant tastes and varied active ingredients have made a substantial effect on global cooking techniques. The intro of seasonings such as turmeric extract, cumin, and coriander has not only improved the taste of various dishes but also added to the health awareness amongst food fanatics.
Dining establishments including Indian-inspired menus have emerged in many nations, mixing typical dishes with regional ingredients to create innovative fusion recipes. In addition, the increase of vegetarianism and veganism has click to investigate even more pushed Indian food into the limelight, as lots of standard Indian recipes are normally plant-based.
Cooking celebrations celebrating Indian food are currently widespread, enabling chefs and home chefs alike to explore its intricacy. The international influence of Indian cuisine appears in the adjustment of its tastes and strategies, cultivating cross-cultural cooking exchanges and improving the global food landscape.
Frequently Asked Inquiries
What Are the Wellness Conveniences of Indian Spices?
Indian spices use different health advantages, including anti-inflammatory buildings, enhanced food digestion, improved resistance, and prospective cancer-fighting results. Their rich anti-oxidants contribute to overall health, promoting heart health and wellness and aiding in weight monitoring.
How Can I Make Indian Food in the house?
To make Indian food in the house, one should collect vital spices, fresh components, and adhere to conventional dishes. Try out flavors and strategies can boost the cooking experience, producing genuine and tasty meals.
Exist Vegetarian Options in Indian Cuisine?

What Is the Background Behind Indian Cuisine?
Indian food's background spans hundreds of years, influenced by regional active ingredients, cultural exchanges, and colonization. Its advancement shows varied practices and methods, causing a rich tapestry of flavors and cooking strategies across the subcontinent.
Exactly how Do I Couple Indian Food With Beverages?
To pair Indian food with beverages, one must consider the dish's flavor degree and taste profile, commonly enhancing it with lassi, chai, or regional red wines, improving the total eating experience with well balanced tastes. - JAIPORE Xpress
Indian cuisine is a complicated mosaic, identified by its abundant seasonings and varied local flavors. While many cuisines rely on a minimal array of flavors, Indian food is differentiated by its varied and extensive array of spices. Both South and north Indian foods share an abundant heritage, they use distinct flavors, components, and cooking methods that mirror their diverse local impacts. The vibrant tapestry of Indian cuisine is woven together by an amazing range of components and spices, each contributing to the nation's cooking variety. As Indian food continues to acquire popularity worldwide, its rich tastes and varied components have made a significant impact on worldwide culinary practices.